Nature Chemistry


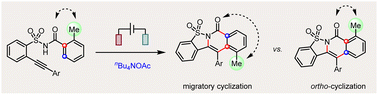
Efficient control over several possible reaction pathways of free radicals is the chemical basis of their highly selective transformations. Among various competing reaction pathways, sulfonimidyl radicals generated from the electrolysis of 2-alkynylbenzenesulfonamides undergo cascade migratory or ortho-cyclization cyclization selectively.
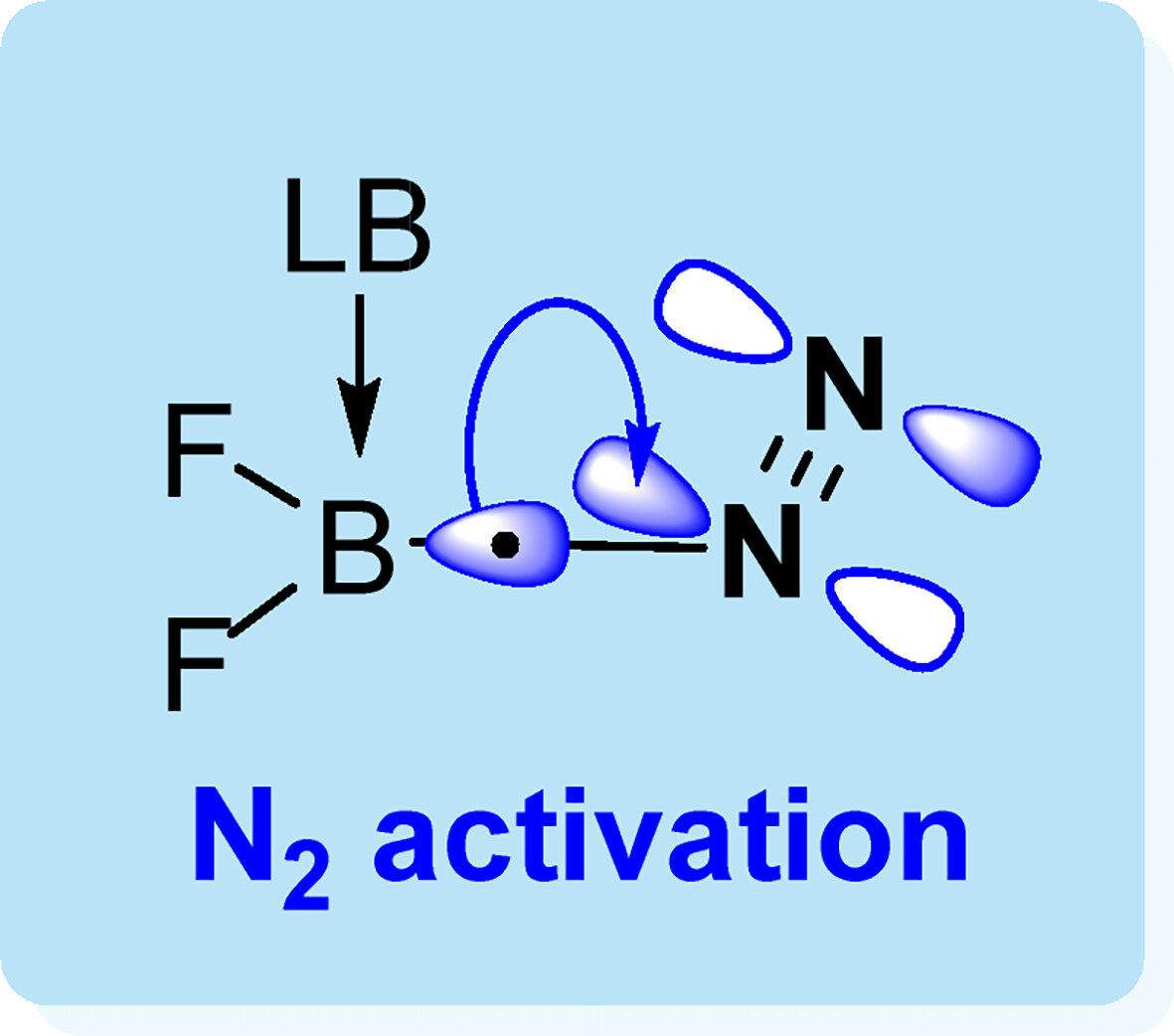
The activation of dinitrogen is significant as nitrogen-containing compounds play an important role in industries. However, the inert NN triple bond caused by its large HOMO-LUMO gap (10.8 eV) and high bond dissociation energy (945 kJ mol−1) renders its activation under mild conditions particularly challenging. Recent progress shows that a few main group species can mimic transition metal complexes to activate dinitrogen. Here, we demonstrate that a series of seven-electron (7e) boron-centered radical can be used to activate N2 via density functional theory calculations.
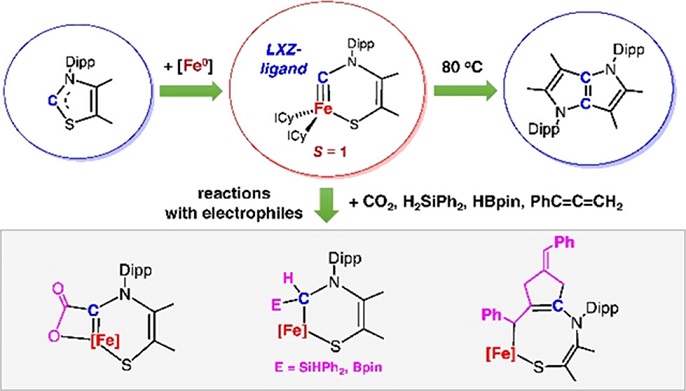
Tuning the spin state of metal carbynes, which have broad applications in organic synthesis and material science, presents a formidable challenge for modern chemists as the strong field nature of carbyne ligands dictates low-spin ground spin states (S = 0 or 1/2) for known metal carbynes. Through the oxidative addition reaction of a low-coordinate iron(0) N-heterocyclic carbene complex with the C−S bond of a thioazole-2-ylidene, we synthesized the first triplet (S = 1) metal terminal carbyne, an iron cyclic carbyne complex.
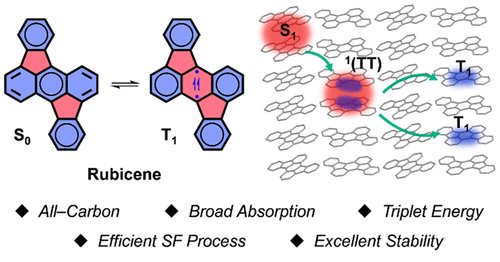
Singlet fission (SF) processes hold great potential in boosting conversion efficiency of solar cells. However, practical applications were greatly hindered by the limited availability of suitable SF materials. Current studies mainly focus on acene derivatives, which are known to be subjected to knotty stability issues or low energy levels. Therefore, developing efficient and stable SF materials is a primary issue before the implementation of practical application. Herein, we present a new SF material based on a rubicene (Rc) skeleton as a desirable acene alternative.
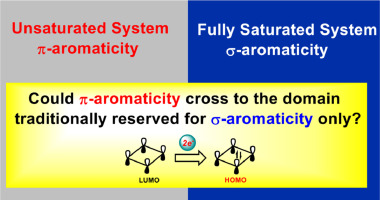
The classification of π-/σ-aromaticity depends on the electrons with the dominating contributions. Traditionally, π- and σ-aromaticity are used to describe the unsaturated and saturated systems, respectively. Thus, it is rarely reported that π-aromaticity is dominated in a saturated system. Here we demonstrate that π-aromaticity could be dominating in several fully saturated four-membered rings (4MRs), supported by various aromaticity indices including ΔBL, NICS, EDDB, MCI, and AdNDP.
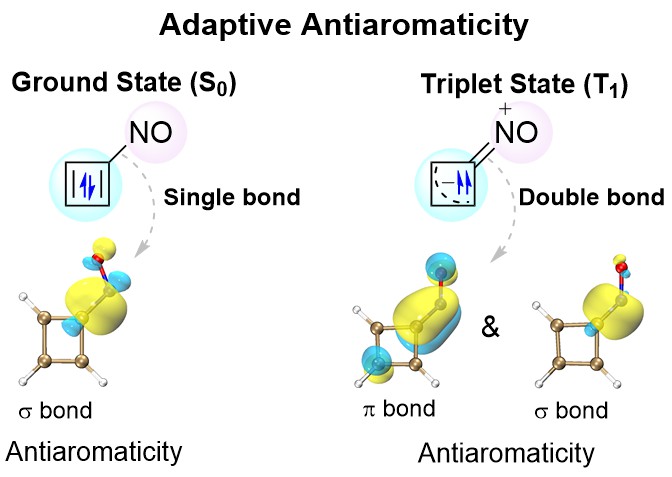
Cyclobutadiene (CBD) displays aromaticity in the lowest-lying triplet excited state (T1) according to Baird's 4n electron rule. Hence, antiaromatic CBD in the T1 state has never been reported so far. Here we demonstrate via density functional theory (DFT) calculations that the CBD ring could possess dual antiaromaticity in the lowest singlet state (S0) and T1 states (termed as adaptive antiaromaticity), which is supported by various aromaticity indices including NICS, ACID, ΔBL, ELF and ISE.
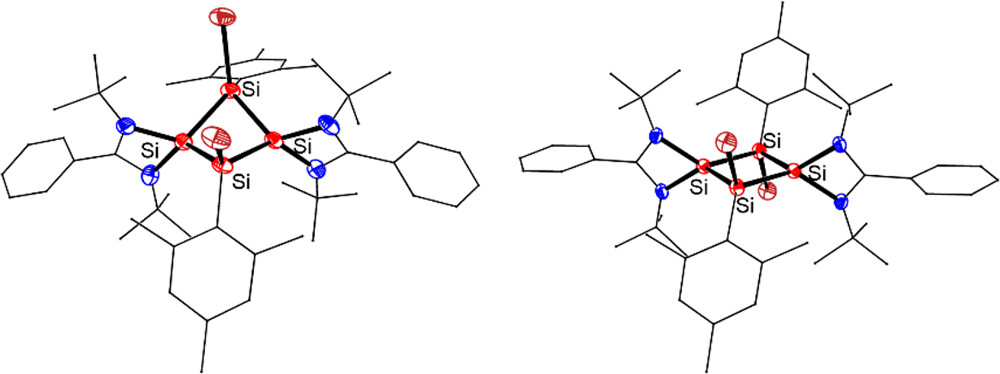
The synthesis, structures, and reactivity of the first neutral 2π-aromatic Si4 rings [LSiSiAr(X)]2 (3: X = Br; 4: X = Cl; L = PhC(NtBu)2, Ar = 2,4,6-Me3C6H2) were described. Compounds 3 and 4 were obtained by 1,3-halogenation of tetrasilacyclobutadiene (LSiSiAr)2 (2), which was prepared by the reductive cross-coupling of trisilane (ArSiCl2)2SiHAr with two equiv of chlorosilylene LSiCl.
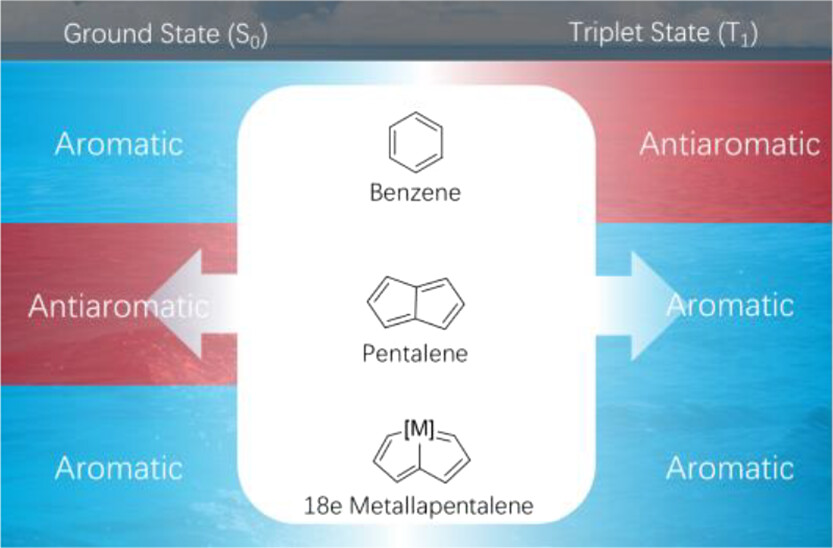
Complexes with aromaticity in both the lowest singlet state (S0) and the lowest triplet state (T1) (denoted as adaptive aromaticity) are rare because according to Hückel’s and Baird’s rules, a species could be aromatic in either the S0 or T1 state in most cases. Thus, it is particularly challenging to design species with adaptive aromaticity. Previous reports on adaptive aromaticity were mainly focused on 16e metallapentalenes.
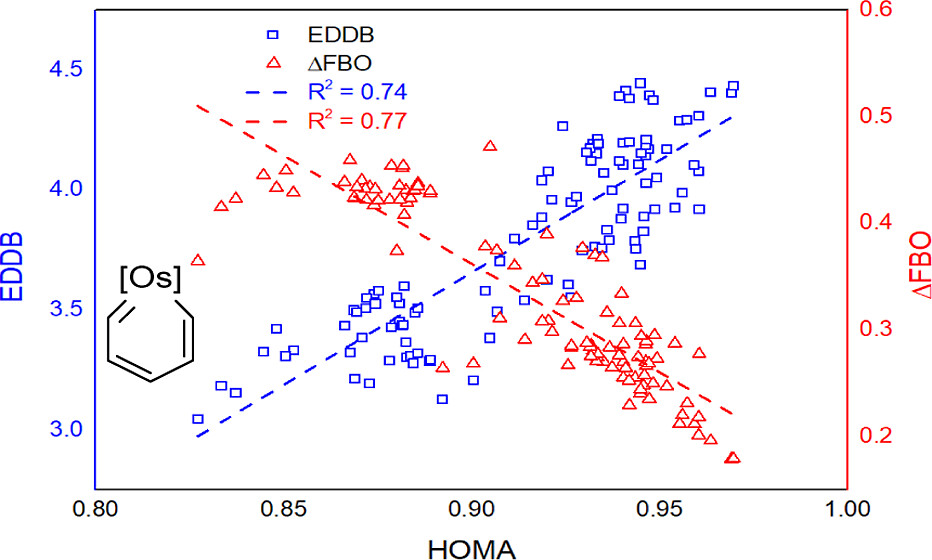
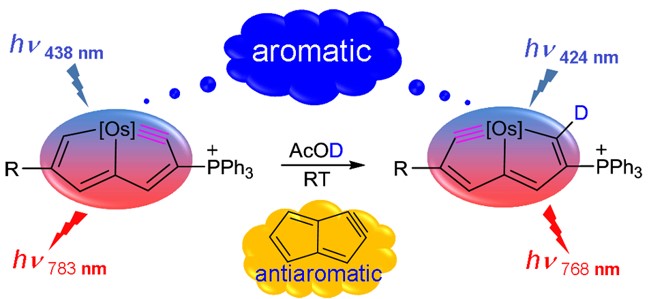
Aromaticity is an important concept in chemistry with multidimensional properties, attracting considerable attention from both experimental and computational chemists. Among various aromaticity indices, the harmonic oscillator model of aromaticity (HOMA) is a reliable aromaticity criterion with a negligible computational cost based on the geometry (bond distance). However, the HOMA parameters for organometallic aromatics are not available. Here, we develop the Os–C bond parameter of HOMA by theoretical calculations.
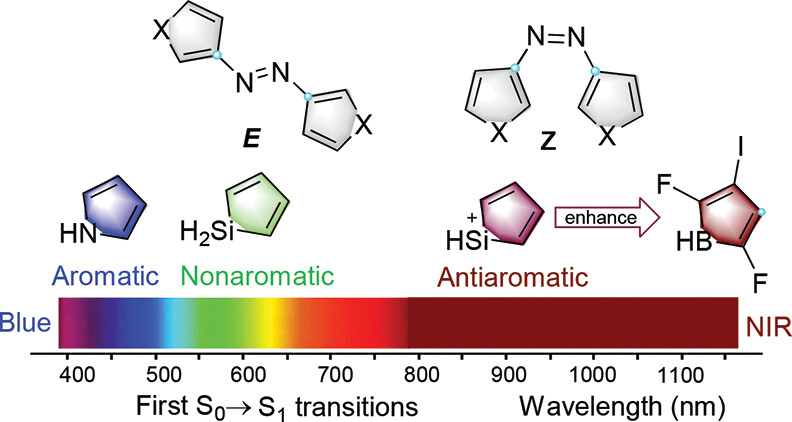
The photoswitching behaviors of heteroaryl azos and azobenzenes have attracted considerable interest due to their applications from material science to pharmacology. However, the use of UV light limits their application, especially in biomedicine and photopharmacology. In this work, using several aromaticity descriptors, including anisotropy of the induced current density analysis and nucleus-independent chemical shifts, we systematically investigate the relationship between anti-aromaticity and the absorption of a series of heterocyclic azos.
Copyright © 2025,
Theme Originally Created by Devsaran
