Quantitative Singlet Fission in Highly Stable Rubicene Skeleton: A Desirable Alternative to Acene Derivatives
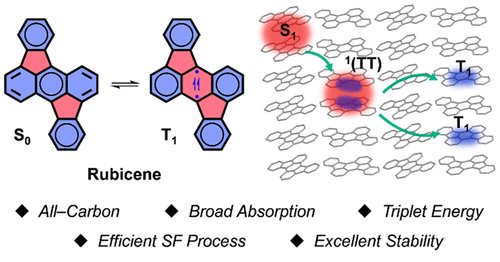
Singlet fission (SF) processes hold great potential in boosting conversion efficiency of solar cells. However, practical applications were greatly hindered by the limited availability of suitable SF materials. Current studies mainly focus on acene derivatives, which are known to be subjected to knotty stability issues or low energy levels. Therefore, developing efficient and stable SF materials is a primary issue before the implementation of practical application. Herein, we present a new SF material based on a rubicene (Rc) skeleton as a desirable acene alternative. Spectroscopic and theoretical results highlight that Rc holds broad absorption, suitable triplet energy, efficient SF process, and excellent stability, which could be ascribed to the distinctive π-sextet resonance structures in the ground state and excited state featuring characteristic aromaticity. Our outcomes not only provide a robust SF system but also offer insights into modular aromaticity in polycyclic systems, which could be used to develop new optical function materials.
