Cobalt-catalyzed migratory carbon-carbon cross-coupling of borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane (9-BBN) borates
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Sat, 08/31/2024 - 08:58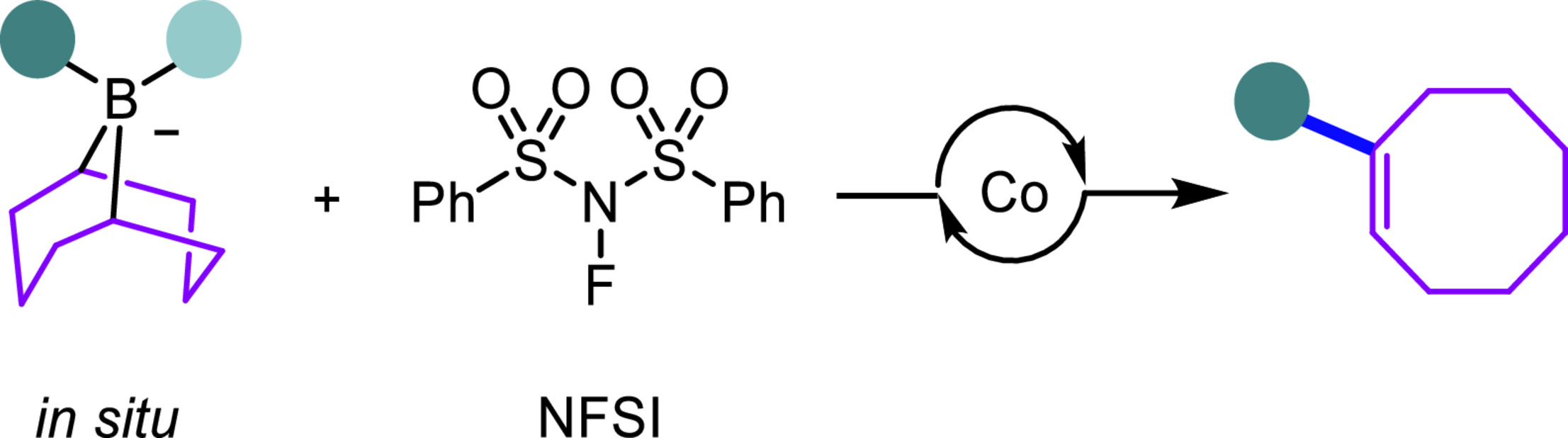
In most Suzuki-Miyaura carbon-carbon cross-coupling reactions, the borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane scaffold (9-BBN) only serves as an auxiliary facilitating the transmetalation step and thus is transformed into by-products. There are rare examples where the 9-BBN derivatives serve as the potentially diverse C8 building blocks in cross-coupling reactions. Herein, we report a cobalt-catalyzed migratory carbon-carbon cross-coupling reaction of the in situ formed 9-BBN ate complexes to afford diverse aryl- and alkyl-functionalized cyclooctenes.