Nature Chemistry


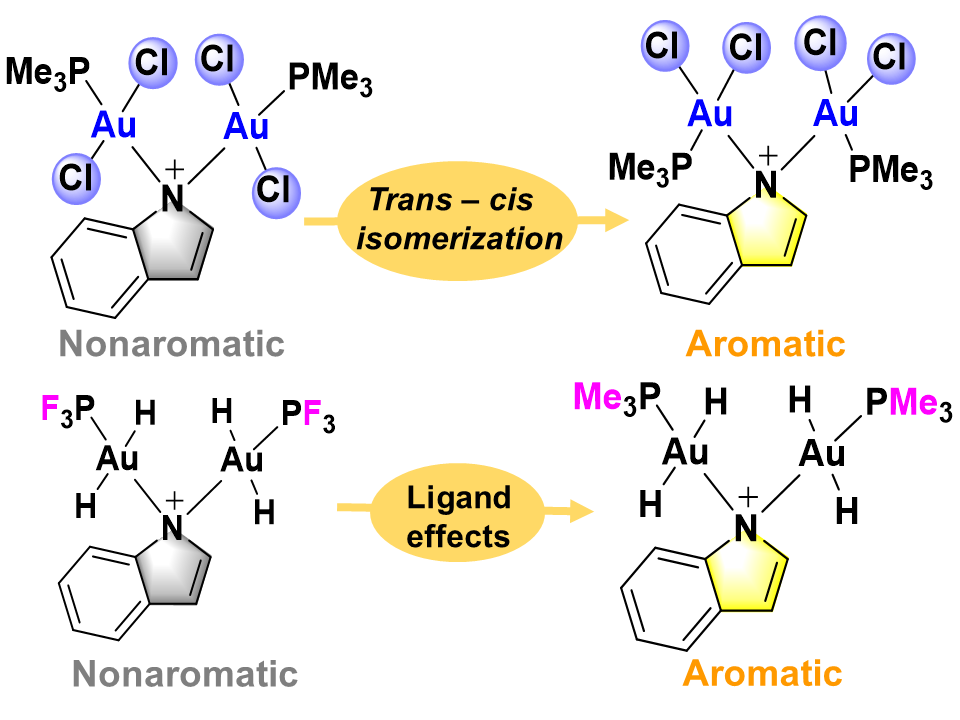
As a fundamental concept in chemistry, aromaticity has been extended from traditional organics to organometallics. Similarly, hyperconjugative aromaticity (HCA) has also been developed from main group to transition metal systems through the hyperconjugation of the substituents. However, it remains unclear that how the oxidation state of transition metal in the substituents affects the HCA. Herein, we demonstrate via density functional theory calculations that HCA could disappear in indoliums when the Au(I) substituents are changed to the Au(III) ones.
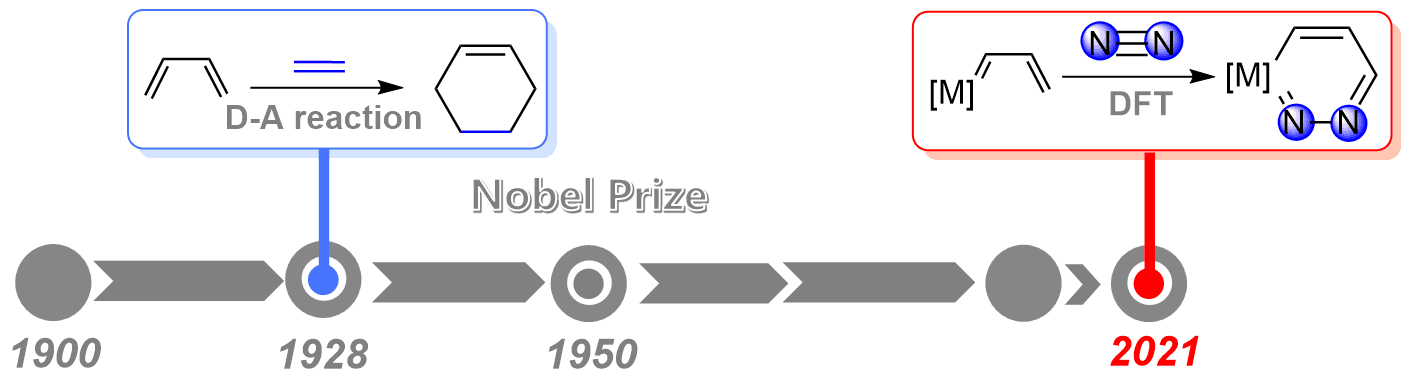
As the strongest triple bond in nature, the N≡N triple bond activation has always been a challenging project in chemistry. On the other hand, since the award of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950, Diels‐Alder reaction has served as a powerful and widely applied tool in the synthesis of natural products and new materials. However, the application of Diels‐Alder reaction to dinitrogen activation remains less developed.
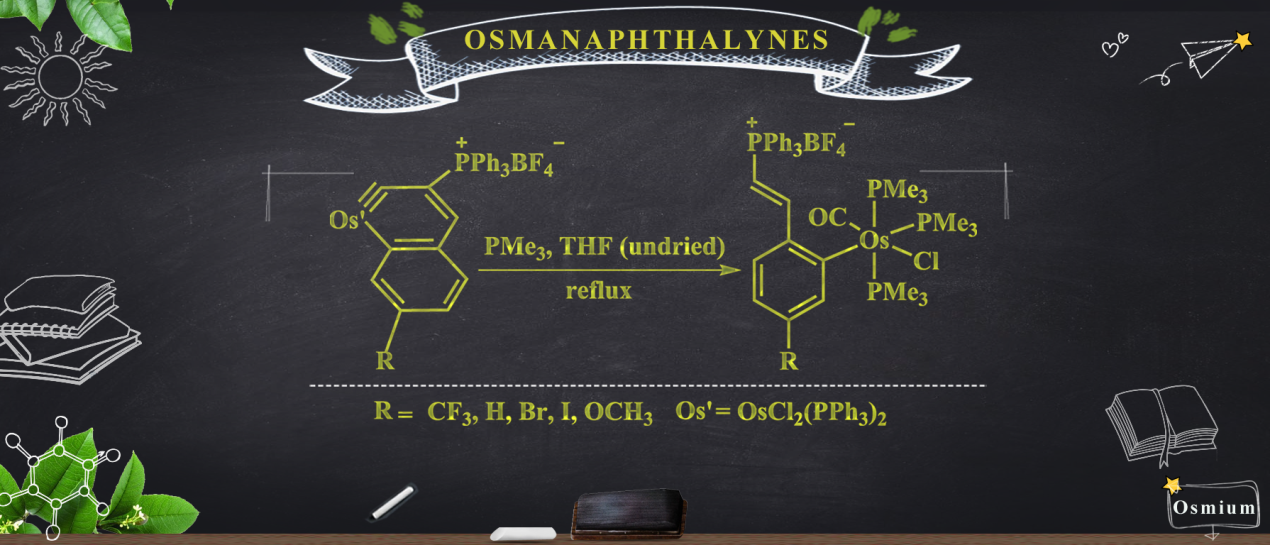
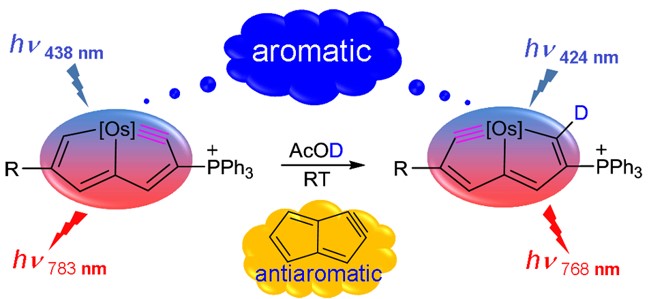
Members of a new class of complexes, 2(CF3), 2(H), 2(Br), 2(I), and 2(OCH3), have been synthesized by a one-pot method involving the treatment of osmanaphthalynes bearing corresponding substituents (1(CF3), 1(H), 1(Br), 1(I), and 1(OCH3) with trimethylphosphine (PMe3) and water (H2O).

The first Ge(0)–Ge(II) germylone–germylene-paired Ge2 complex (LSi)2Ge2 (4) and the molecular Ge4 cluster (LSi)2Ge4 (5) supported by the chelating carbanionic ortho-C,C′-dicarborandiyl-silylene ligand LSi [L = C,C′-C2B10H10, Si = PhC(tBuN)2Si] have been synthesized and isolated via reduction of the corresponding precursors chlorogermyl-germyliumylidene chloride (2), [(LSi)2Ge(Cl)Ge]+Cl–, and (LSi
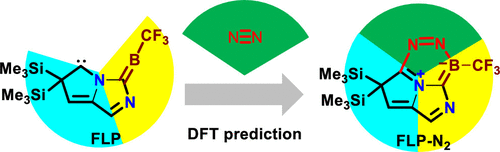
Activation of atmospherically abundant dinitrogen (N2) by metal-free species under mild reaction conditions has been one of the most challenging areas in chemistry for decades. Very recent but limited progress in N2 activation by boron species, including two-coordinated borylene and methyleneborane and three-coordinated borole and borane, has been made toward metal-free N2 activation.
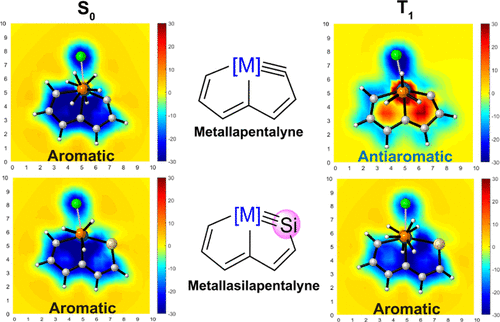
Cyclic molecules with 4n + 2 or 4n electrons are aromatic in the lowest singlet state (S0) or the lowest triplet state (T1) according to Hückel and Baird’s rules. Thus, the design of aromatic species in both the S0 and T1 states (termed as adaptive aromaticity) is particularly challenging. In this work, we demonstrate that metallasilapentalynes show adaptive aromaticity supported by structural, magnetic, and electronic indices, in sharp contrast to metallapentalynes, which exhibit aromaticity in the S0 state only.
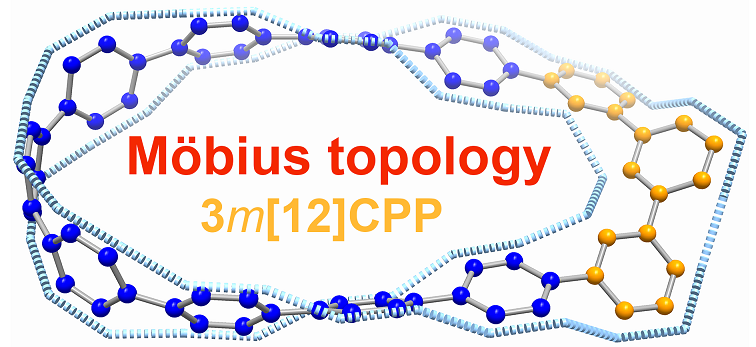
Carbon nanohoop, a class of constrained molecular architecture consisting of linked arene units, has attracted considerable interest from both experimental and theoretical chemists due to their synthetic challenge and aesthetic architectures. Another fascinating and synthetically challenging species, the Möbius-type molecule, has been attracting the scientific community with its elegant structure and aromaticity. Thus, combining two things together, synthesizing a carbon nanohoop with Möbius topology remains more challenging to date.

The first Zintl cluster containing a distorted Bi6 triangular prism, [Bi6Mo3(CO)9]4−, has been synthesized and structurally characterized. Quantum chemical calculations indicated that the distorted cage cluster features multiple local σ-aromaticity.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/CC/D1CC00734C#!divAbstract
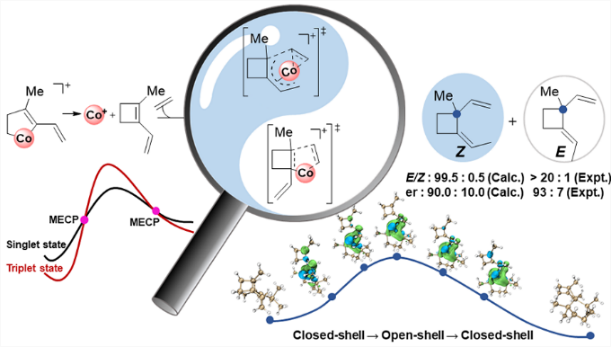
The cyclobutane unit is important to prepare complex natural products with biological activity due to the high ring strain. Among various approaches, [2 + 2] cycloaddition is one of the major strategies to prepare cyclobutane under light conditions. Recently, Rajanbabu's group reported tandem catalysis for asymmetric coupling of inactivated ethylene and enynes to functionalized cyclobutenes or cyclobutanes. However, the reaction mechanisms remain unproven.

Aromaticity and hyperconjugation are two fundamental concepts in organic chemistry. By combination of the two concepts together, the resulting hyperconjugative aromaticity has attracted considerable attention from both theoretical and computational chemists. However, previous studies are mainly focused on the main group chemistry. For the hyperconjugative aromaticity in the transition metal chemistry, the studies are limited to groups 10 and 11.
Copyright © 2025,
Theme Originally Created by Devsaran
