Solvent-driven Interconversion of Pyridine Dicarbanion-bonded Ag13 Nanocluster Isomers
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Fri, 04/25/2025 - 20:12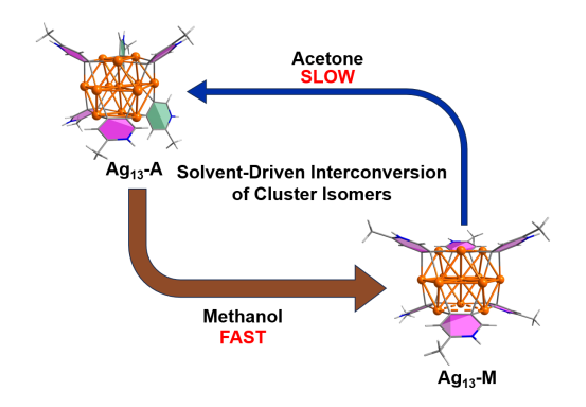
Solvent screening is pivotal in the optimization of reaction conditions for metal-catalyzed reactions. However, to date little is known about the role of solvent effects in driving in situ structural evolution of metal-containing species towards polynuclear organometallic cluster intermediates and determining their reactivity. We herein isolate two distinct thirteen-membered silver cluster isomers, Ag13-A and Ag13-M, in acetone and methanol, respectively.