Aromaticity‐promoted CO2 Capture by P/N‐Based Frustrated Lewis Pairs: A Theoretical Study
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Thu, 12/19/2019 - 02:25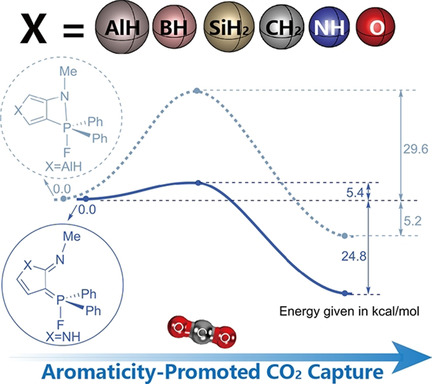
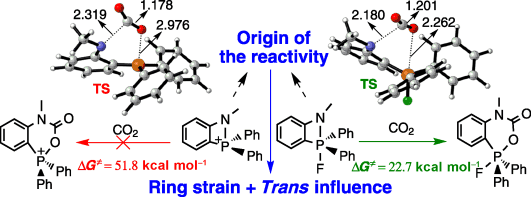
Carbon dioxide (CO2, a common combustion pollutant) releasing continuously into the atmosphere is primarily responsible for the rising atmospheric temperature. Therefore, CO2 sequestration has been an indispensable area of research for the past several decades. On the other hand, the concept of aromaticity is often employed in designing chemical reactions and metal‐free frustrated Lewis pairs (FLPs) have proved ideal reagents to achieve CO2 reduction. However, considering FLP and aromaticity together is less developed in CO2 capture.