Reactions of [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)](+) with dihydrogen, silanes, olefins, alkynes, and allenes
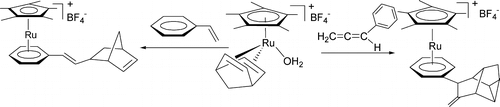
Formal [2+2+2] addition reactions of the NBD ligand in [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 (NBD = norbornadiene) with H-2, Ph3SiH, ArCH=C=CH2, and RC=-CPh were observed. In contrast, olefins such as styrene and NBD do not undergo similar [2+2+2] addition reactions with [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4. [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 reacts with H-2 in benzene to give [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-C6H6)]BF4 and nortricyclene. Similarly, [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 reacts with Ph3SiH to give [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-C6H5SiPh2OH)]BF4 and nortricyclene. Treatment of [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 with styrene produces [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-C6H5-CH=CHC7H9)]BF4, [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-C6H5-CH=CH2)]BF4, C6H5-CH=CH-C7H9, and Cp*Ru(eta(5) -C5H4-C9H11). The latter complex is also produced from the reaction of [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 with NBD. Treatment of [Cp*Ru(H2O)(NBD)]BF4 with ArCH=C=CH2 produces [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-Ar-C10H11)]BF4. Reactions of [Cp*Ru(H2O)- (NBD)]BF4 with RC=CC6H5 (R = Ph, Me) give [Cp*Ru(eta(6)-C6H5-C10H8R)]BF4. The reaction pathways of the coupling reactions have been studied by computational chemistry.
