Insertion reactions of allenes with palladium aryl complexes [PdI(Ph)(PPh3)](2) and PdI(Ph)(dppe)
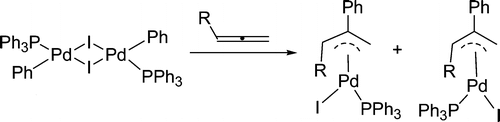
Treatment of [PdI(Ph)(PPh3)]2 with allenes CH2═C═CHR (R = CMe3, CO2Et, P(O)(OEt)2, and SO2Ph) in dichloromethane at room temperature produces a mixture of cis and trans isomers of the π-allyl palladium complexes PdI(η3-CH2C(Ph)CHR)(PPh3) in which the R group is anti to the Ph group. The disubstituted allenes MeCH═C═CHR (R = P(O)(OEt)2 and SO2Ph) similarly react with [PdI(Ph)(PPh3)]2 to give the π-allyl palladium complexes PdI(η3-MeCHC(Ph)CHR)(PPh3) in which the R group is anti and the Me group is syn to the Ph group. PdI(Ph)(dppe) alone was found to be unreactive toward allenes such as CH2═C═CHSO2Ph and MeCH═C═CHSO2Ph at room temperature. In contrast, in the presence of TlPF6, PdI(Ph)(dppe) readily reacts with allenes CH2═C═CHR (R = CMe3, CO2Et, COPh, and SO2Ph) and MeCH═C═CHSO2Ph to give the π-allyl palladium complexes [Pd(η3-CH2C(Ph)CHR)(dppe)]PF6 and [Pd(η3-MeCHC(Ph)CHR)(dppe)]PF6, respectively. Although mechanistically possible, vinyl complexes were not observed as the insertion products in all cases. The substituents of allenes appear to have no effect on the reaction pathways, at least for the allenes used in this study. The insertion reactions involving PdI(Ph)(PR3)(allene) have been studied by computational chemistry using the model complex PdI(Ph)(MeCH═C═CHSO2H)(PH3).
