Static polarizabilities of copper cluster monocarbonyls CunCO (n=2-13) and selectivity of CO adsorption on copper clusters
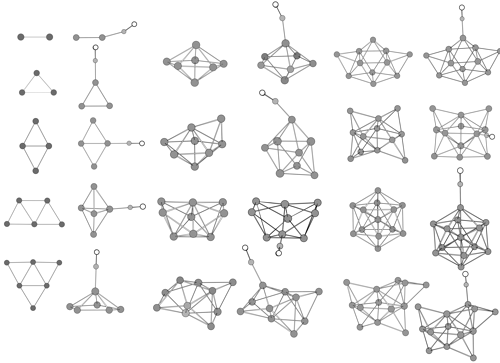
Density functional calculations for copper clusters Cu and their monocarbonyls CunCO (n less than or equal to 13) have been performed using the relativistic ECP plus DZ basis set augmented by an f polarization function for copper atom. Equilibrium geometries, harmonic frequencies, and static mean polarizabilities of Cu-n and CunCO are determined. The feature of CO adsorption on the copper cluster and the effect of CO adsorption on stability and polarizability of the cluster are investigated. Calculations show that CO adsorption on copper clusters is selective in terminal coordination, and the favored adsorption sites are dominated by the local orientation of relevant frontier orbitals and the distribution of overall electrostatic potential surfaces of copper clusters. The interaction of Cu-n with CO in the copper cluster carbonyls leads to significant odd-even variations of the static polarizability differences between Cu CO and the separated components Cu-n and CO. Size dependences of cohesive energies, CO binding energies, and static mean polarizabilities have been explored.
